What is Wind?
Wind is simply air in motion. It is caused by the uneven heating of the earth’s surface by radiant energy from the sun. Since the earth’s surface is made of very different types of land and water, it absorbs the sun’s energy at different rates. Water usually does not heat or cool as quickly as land because of its physical properties. An ideal situation for the formation of local wind is an area where land and water meet.
During the day, the air above the land heats up more quickly than the air above water. The warm air over the land expands, becomes less dense and rises. The heavier, denser, cool air over the water flows in to take its place, creating wind. I n the same way, the atmospher ic winds that circle the ear th are created because the land near the equator is heated more by the sun than land near the North and South Poles. Today, people use wind energy to make electricity. Wind is called a renewable energy source because the wind will blow as long as the sun shines.
Wind Direction
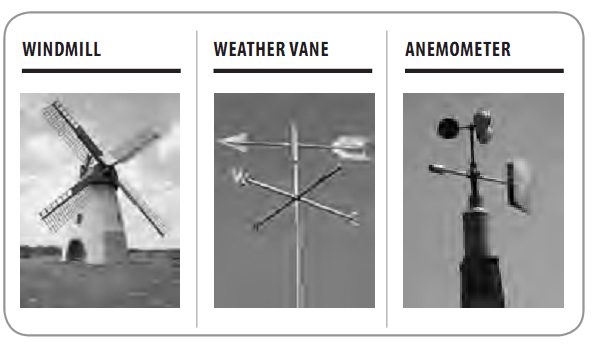
A weather vane, or wind vane, is used to show the direction of the wind. A wind vane points toward the source of the wind. Wind direction is reported as the direction from which the wind blows , not the direction toward which the wind moves. A north wind blows from the north toward the south.
Wind Production
Every year, wind produces only a small amount of the electricit y this country uses, but the amount is growing every year.
One reason wind farms don’t produce more electricity is that they can only run when the wind is blowing at certain speeds. In most places with wind farms, the wind is only optimum for producing electricit y about three -fourths of the time. ( That means most turbines run 18 hours out of 24.)